🚀 Deploying Applications on Docker Swarm #
Docker Swarm is a native container orchestration tool that allows you to deploy and manage containerized applications across a cluster of Docker nodes with ease. Understanding the core concepts helps you grasp how your application runs inside the Swarm.
Source: Docker Documentation
📦 Core Concepts #
Docker Swarm operates with four key hierarchical components:
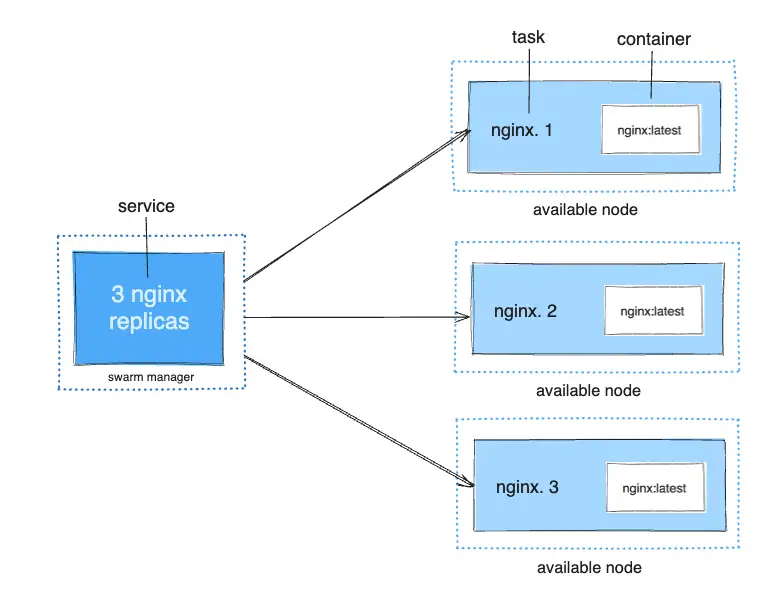
1. Container #
- The actual running instance of your application image
- Similar to a pod container in Kubernetes
- Executes the application code and its dependencies
- Isolated from other containers but shares the host OS kernel
2. Task #
- A Swarm-managed unit of work that runs exactly one container
- The atomic scheduling unit in Swarm
- Has a lifecycle: assigned → prepared → running → complete (or failed)
- If a task fails, the scheduler creates a new task to maintain the desired state
3. Service #
- A declarative definition of an application running in the Swarm
- Specifies how many copies (tasks) of a container to run
- Defines the container image, ports, networks, volumes, and resource constraints
- Two service modes:
- Replicated: Run a specified number of replicas across the cluster
- Global: Run one task on every node in the cluster
4. Stack #
- A collection of related services deployed together
- Defined by a single Docker Compose file
- Simplifies managing multiple services as a single unit
- Includes networks and volumes required by the services
🔄 Service Deployment Workflow #
When you deploy a service to Docker Swarm, the following happens:
- Define Service: You specify the container image, number of replicas, and other parameters
- Service Creation: The Swarm manager accepts the service definition
- Task Scheduling: The scheduler assigns tasks to available worker nodes
- Container Creation: Each worker node creates containers for its assigned tasks
- Service Discovery: The internal DNS registers the service for discovery by other services
- Load Balancing: Incoming requests are distributed across all tasks of the service
📝 Example: Deploying a Web Application #
# docker-compose.yml for a web application stack
version: '3.8'
services:
web:
image: nginx:latest
deploy:
replicas: 3
update_config:
parallelism: 1
delay: 10s
restart_policy:
condition: on-failure
ports:
- "80:80"
networks:
- webnet
database:
image: postgres:13
environment:
POSTGRES_PASSWORD: example
volumes:
- db-data:/var/lib/postgresql/data
networks:
- webnet
deploy:
placement:
constraints:
- "node.role==worker"
networks:
webnet:
volumes:
db-data:
🛠️ Common Commands #
# Deploy a stack
docker stack deploy -c docker-compose.yml myapp
# List all services in a stack
docker stack services myapp
# Scale a service
docker service scale myapp_web=5
# Update a service
docker service update --image nginx:1.21 myapp_web
# Remove a stack
docker stack rm myapp
🔍 Service Inspection and Troubleshooting #
To inspect and troubleshoot services:
# View service details
docker service inspect myapp_web
# View service logs
docker service logs myapp_web
# List tasks for a service
docker service ps myapp_web
# View task logs
docker logs <task-container-id>
Understanding these concepts and commands will help you effectively deploy, manage, and troubleshoot applications on Docker Swarm.